Evaluating the Interaction of Articular Mobility and Balance in Patient Outcomes
Evaluating the Interaction of Articular Mobility and Balance in Patient Outcomes
Blog Article
Articular movement and control are essential elements that influence patient results in rehabilitation and therapy. Joint mobility refers to the extent of movement permitted at a joint, while stability involves the ability to maintain control of that joint during movement. When clients have optimal articular mobility, they can navigate their extremities unrestricted, which is vital for conducting daily tasks. On the other hand, steadiness helps prevent harm by allowing the body to maintain proper positioning and balance during these actions. Grasping how these two elements interact can lead to better treatment plans and enhanced recovery for clients.
In many cases, patients with articular discomfort or traumas often experience a reduction in mobility. For instance, disorders like osteoarthritis can restrict how much a joint can move, making it difficult for individuals to perform activities such as ambulating or climbing stairs. Physical therapists often concentrate on exercises that enhance mobility through flexibility work and fortification. These exercises can help restore the range of motion, making it more manageable for clients to engage in their everyday tasks. Nonetheless, increasing range of motion without accounting for steadiness can lead to additional injuries, highlighting the need for a balanced approach.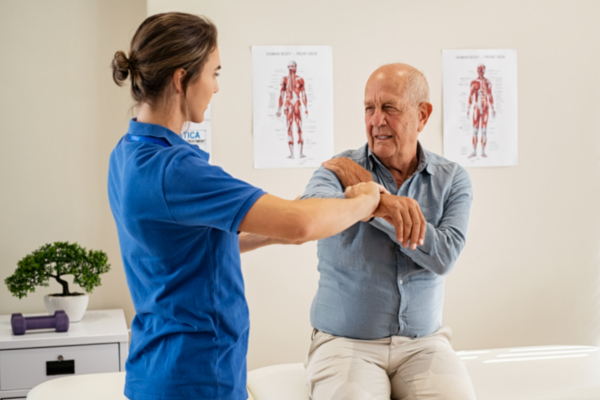
Stability is equally important in rehabilitation. When a joint is deficient in stability, it becomes more susceptible to harm during movement. For instance, an unstable knee articulation can result to sprains or ruptures while running or jumping. To enhance stability, rehabilitation specialists may integrate exercises that fortify the muscles around the joint. These activities help support the joint and avert excess movement more helpful info that could result to injury. By concentrating on both mobility and control, therapists can provide a comprehensive care plan that addresses the specific needs of each client.
The interplay between articular mobility and control is especially evident in athletic rehabilitation. Athletes frequently require a elevated level of both flexibility and control to execute at their best. For instance, a gymnast needs to have Get the facts limber joints to achieve complex movements while also preserving stability to prevent falls. In sports training, coaches and trainers emphasize the significance of cultivating both aspects to improve performance and minimize the risk of harm. This method ensures that athletes can perform effectively while maintaining their joints protected during rigorous exercises.
Ultimately, comprehending the relationship between articular mobility and control can lead to better results for patients in multiple environments, from rehabilitation centers to athletic conditioning facilities. By encouraging both aspects, medical practitioners can help patients recover their power and confidence. This integrated approach not only helps in rehabilitation but also equips individuals with the tools they need to avert future harm. As research progresses to advance in this area, the significance of integrating mobility and control in treatment plans will continue to be a key focus for enhancing patient care and general health.